What is ISO 3691-4 for AGV? The responsibility framework
 Simply put, the ISO 3691-4:2020 outlines the safety requirements for driverless industrial vehicles and their systems (AGVs), as well as how to check that they meet those requirements.
Simply put, the ISO 3691-4:2020 outlines the safety requirements for driverless industrial vehicles and their systems (AGVs), as well as how to check that they meet those requirements.
The 3691-4 also provides critical guidance for stakeholders in the AGV ecosystem. It defines the shared responsibilities of OEM Manufacturers, Integrators, and End Users.
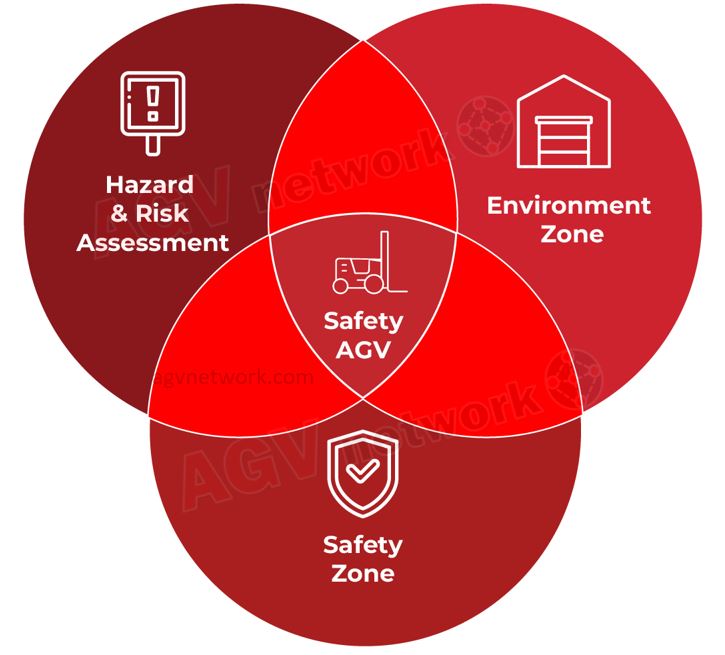
The ISO EN 3691-4 describes three main subjects to reach a SAFE AGV SYSTEM:
✅ The operating environment (i.e. defining the different zones where the truck operates and interacts with humans).
✅ The hazards and risk associated, and
✅ The correct implementation of the Safety (protection) Systems.
ISO 3691-4:2020, though not yet a harmonised standard (so it is not mandatory), marks a crucial advance in autonomous vehicle safety guidelines.
This norm and its implications for each stakeholder create a matrix of co-responsibility that contributes to a unified approach towards AGV safety and residual risk management.
However, ISO 3691-4:2020 should not be seen as a standalone document to assume conformity with other AGV standards and the Machinery Directive.
It's a part of a broader safety ecosystem, suggesting the need for multiple standards to ensure comprehensive safety in evolving autonomous vehicle systems.
By the way, if you wish to have specific details about mobile robot safety, I highly suggest to download this whitepaper with info about scanners, risk zones, risk asessment, etc. Everything packed with great illustrations

Of course, it's free for agvnetwork's registered members ????
| Click here to download the whitepaper |
Let's go ahead
OEM Manufacturers: Crafting a Culture of Safety
Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) sit at the very genesis of the mobile robot lifecycle.
They're responsible for designing and building mobile robots, and their safety obligations are paramount.
AGV Manufacturers must ensure their AGVs are engineered to avoid hazards and mitigate risks right from the outset.
It is mandatory to perform a comprehensive risk assessment about the robot to identify potential hazards associated with AGV use (collision, entrapment, and more), in line with this, OEMs must design and implement safety measures into their products.
However, even if manufacturers strive to design AGVs with the highest safety standards, some level of residual risk always remain.
The role of manufacturers doesn't just end with designing and building AGVs. As per the Machinery Directive (MD), they must also supply extensive documentation.
This is where risk transfer becomes crucial. By working closely with Integrators and End Users, OEMs can help them understand and manage these residual risks, ensuring a safer AGV environment overall.
Integrators: Bridging the Safety Gap
Integrators play a unique role in AGV safety, serving as the intermediary between OEM Manufacturers and End Users.
CE marking is applicable only to the AGV or AMR itself, not the whole system. Hence, the responsibility of ensuring complete installation and identification or mitigation of all risks rests with the integrator.
Integrators should perform their risk assessments, focusing on the interface between AGVs and the end user's environment.
Additionally, Integrators play a significant role in risk transfer. They have the responsibility of communicating any residual risk identified during the integration process to the end user, equipping them with the knowledge to handle potential hazards.
End Users: The Final Guardians of AGV Safety
End Users are the final stakeholders in the AGV safety chain. They must ensure the safe operation of AGVs within their premises and are thus responsible for any associated risks.
This involves conducting their risk assessments, which consider specific use cases and user interactions.
End Users should continuously monitor and manage residual risks and be aware of the risk transfer from the OEM and Integrator.
Safety training for AGV operators is also vital, ensuring they understand how to operate the machines safely and are aware of potential hazards.
This includes adequate training, enforcing zone access control, and supplying employees with required Personal Protective Equipment (PPE).
Furthermore, as AGV standards, such as ISO 3691-4, state, end users are obligated to use and maintain the AGVs as per the manufacturer's guidelines.
Any misuse or lack of maintenance can heighten the residual risks, pushing the safety of the entire operation into jeopardy.
The Takeaway: Shared Responsibility and Clear Communication
Understanding the shared responsibilities of OEM Manufacturers, Integrators, and End Users is the first step in creating a safe and efficient AGV system.
OEM Manufacturers, Integrators, and End Users all have crucial roles to play in ensuring the safe operation of AGVs. But these roles are not isolated; effective communication and risk transfer between stakeholders is vital.
By embracing their roles and responsibilities, respecting the norms, and conducting thorough risk assessments, stakeholders can reduce residual risks and create a safer AGV environment.
Remember, safety is not just a box to tick, but an ongoing, collaborative effort.
|
Even if the 3691-4 is not obligatory, I would not buy a mobile robto that does not comply with. They reflect the manufacturer seriousness, as well as ensure safer vehicles, a key factor when choosing a mobile robot supplier. |
It does not matter if you are a manufacturer, integrator or end user, make sure you have a copy of the safety standards.

American National Standards InstituteISO 3691-4:2020
EU StandardANSI/ITSDF 56.5-2019
American StandardIndustrial Trucks - Safety Requirements And Verification - Part 4: Driverless Industrial Trucks And Their Systems Safety Standard For Guided Industrial Vehicles Industrial Mobile Robots - Safety Requirements - Part 1: Requirements For The Industrial Mobile Robot $200 $35 $225 


Note: The B56.5 and the 3691-4 are suitable for AGVs while the B15.08 is applicable for Industrial Mobile Robots.
|
Related articles
AGV Sensors : 101: A Beginner's Guide to the Most Important Components
AGV Navigation Methods: A comprehesive guide to understand how do mobile robots navigate
Types of Automated Guided Vehicles
Automated Guided Vehicles Cost : Discovering the cost elements in a mobile robot project |
 Written by Alfredo Pastor Tella (agvnetwork editor).
Written by Alfredo Pastor Tella (agvnetwork editor).
Follow me on LinkedIn... let's create a mobile robot community to discuss and learn about these outstanding systems.




